How To Optimize For Search Intent-SEOGuideLab
Introduction
Most businesses make the common mistake of targeting keywords without fully understanding search intent analysis. If you're doing this, you're setting yourself up for failure. The truth is, user intent is at the heart of SEO success. Understanding what a user truly wants when they type a query into Google is the secret to ranking higher and driving more targeted traffic.
Why Understanding Search Intent is Key to SEO Success
Google's algorithm is designed to rank content that best satisfies the SEO search intent. It's not enough to simply optimize a page for a keyword — you need to make sure the content matches the specific intent behind that keyword.
Here’s how you can optimize your SEO strategy by understanding and leveraging search intent.
How to Optimize for Search Intent
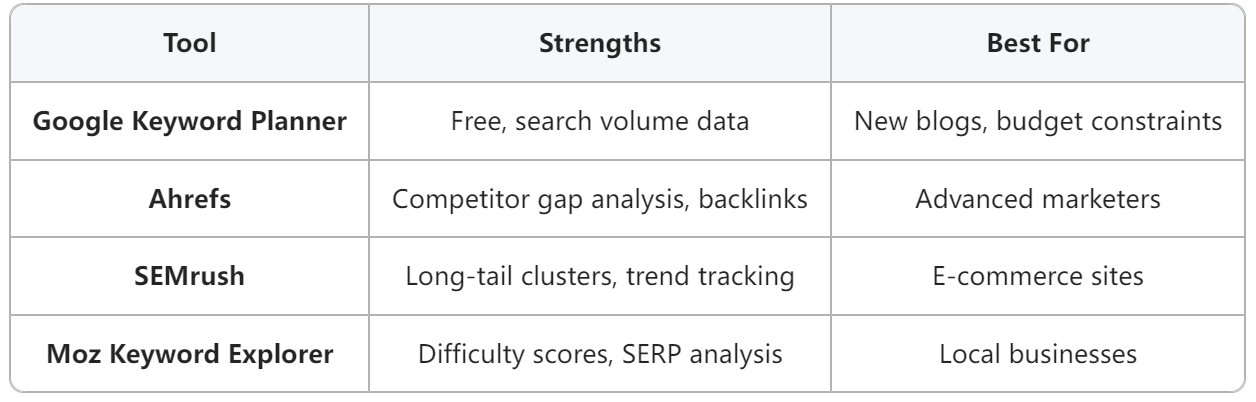
1. Start with Keyword Research
Keyword research is the first step in any SEO strategy, but not all keywords are created equal. Many businesses make the mistake of targeting keywords with high search volume without considering how well they match the user intent.
To begin your keyword research, use tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Google Keyword Planner. These tools can help you identify keywords that are relevant to your niche. But don’t stop there — after finding the keywords, organize them in a spreadsheet to better understand their search volume, competition, and, most importantly, their intent.
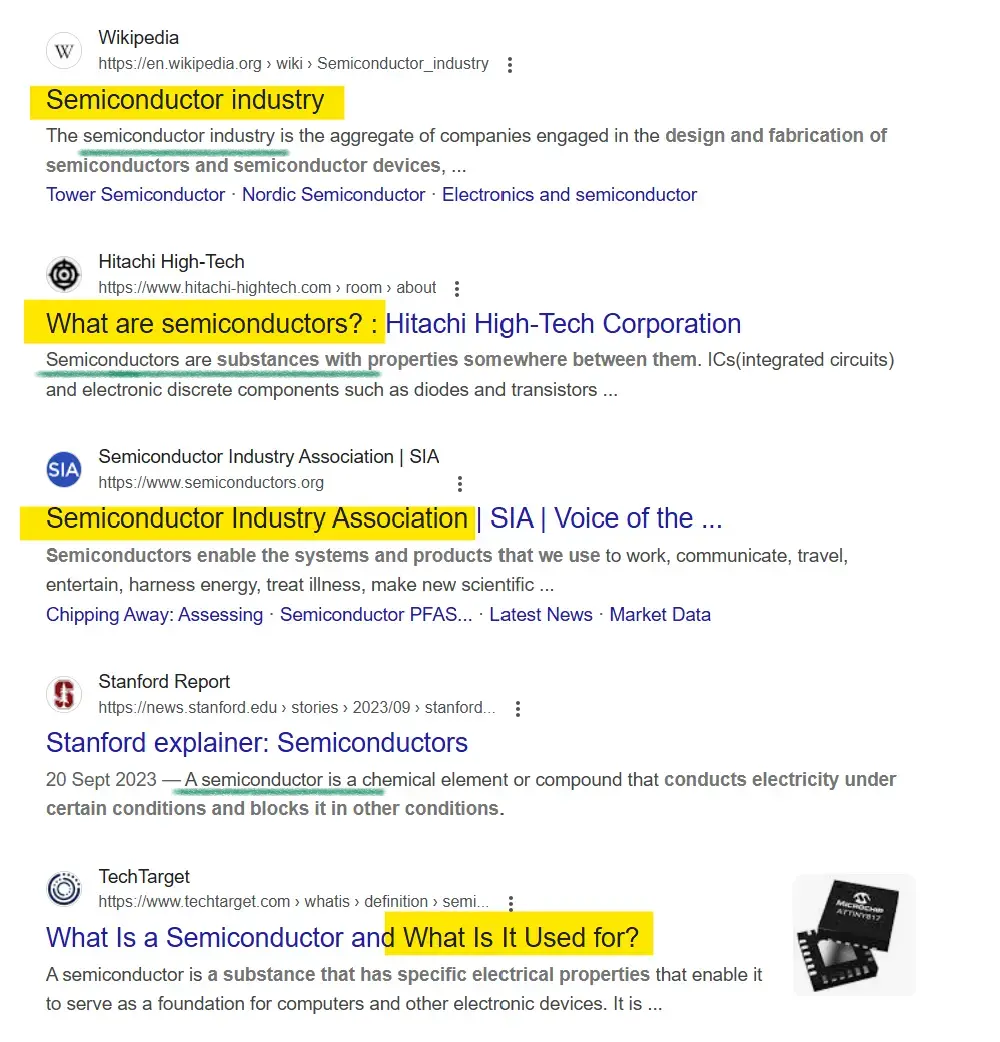
2. Analyze Google's SERPs for Each Keyword
Once you’ve selected a keyword, perform a Google search and analyze the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs). The results at the top of the page are the most relevant, according to Google’s algorithm.
Look closely at the types of pages that rank well. Are they blog posts, product pages, comparison articles, or something else? The nature of these pages will give you clues about the search intent behind the query. For example, if Google is showing product pages for a specific keyword, the user’s intent is likely transactional. If it shows informational articles, the search intent is likely informational.
3. Categorize the Search Intent
Now that you have analyzed the SERPs, it's time to categorize the search intent. Understanding the intent behind a search is critical for aligning your content.
There are four main types of search intent:
Transactional (High Intent):
Users are ready to make a purchase or take action. Keywords like “buy,” “best price,” or “discount” are transactional keywords. If your target keyword falls into this category, you need to optimize landing pages or product pages that drive conversions.
Commercial (Medium Intent):
Users are comparing products or services. These users aren’t ready to buy yet, but they are evaluating their options. Keywords like “best X for Y” or “X vs Y” signal commercial keywords. In this case, comparison guides, reviews, or detailed product pages are ideal.
Informational (Low Intent):
Users are looking to learn more about a topic. Keywords like “how to,” “what is,” or “why does” indicate informational intent. Blog posts, tutorials, and educational content are perfect for targeting these types of queries.
Navigational:
Users are looking for a specific website or brand. These searches are often branded queries like “Facebook login” or “Nike official site.” For these, you need to optimize your homepage and ensure your branding is clear and consistent.
4. Use Google’s Clues to Refine Your Understanding
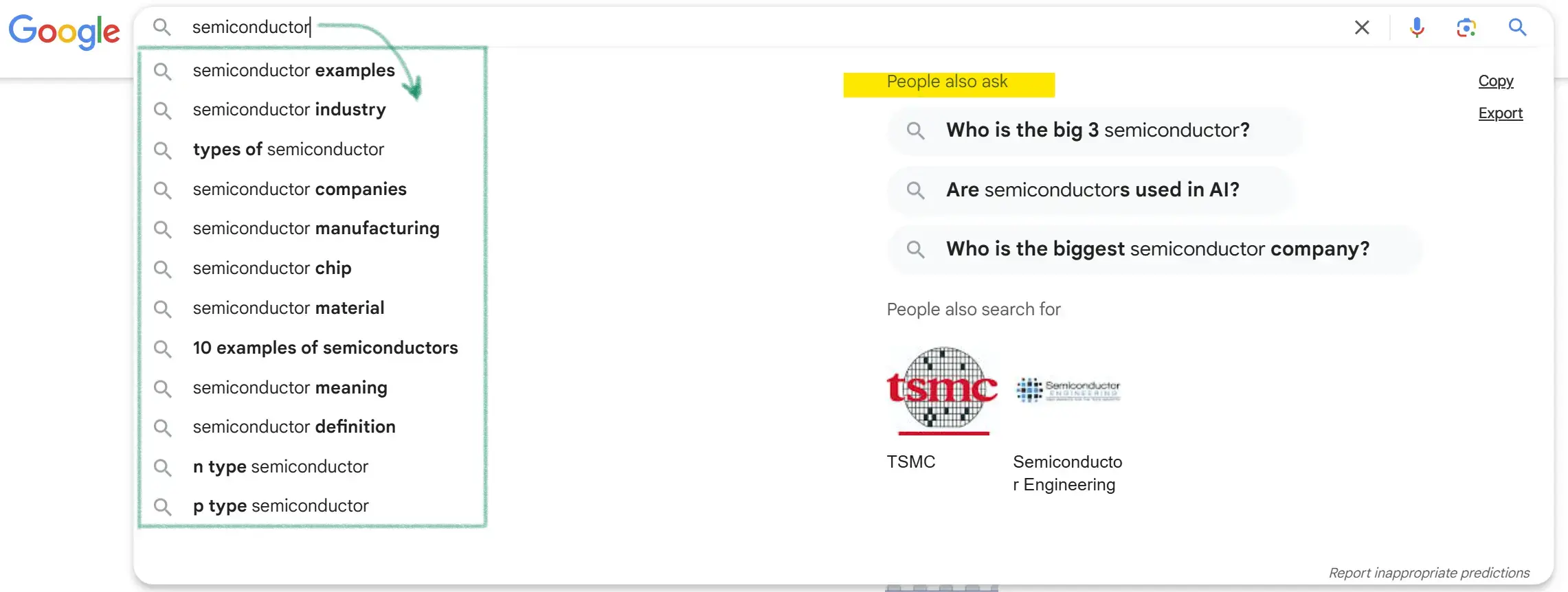
Google provides several helpful clues that can further refine your understanding of search intent:
People Also Ask: These are related queries that show what other users are searching for around your target keyword. It’s a great way to uncover variations of search intent.
Related Searches: At the bottom of the SERPs, you’ll see a list of related searches. These are more signals that can help you understand the broader user intent behind a search query.
AI Overviews: Google’s AI-driven snippets or knowledge panels highlight what Google considers the best answer to a question. Use these to see how Google interprets the intent of the search.
5. Align Your Content to Intent
Once you understand the search intent, it’s time to create content that aligns with it. Here's how to optimize your content for different types of search intent:
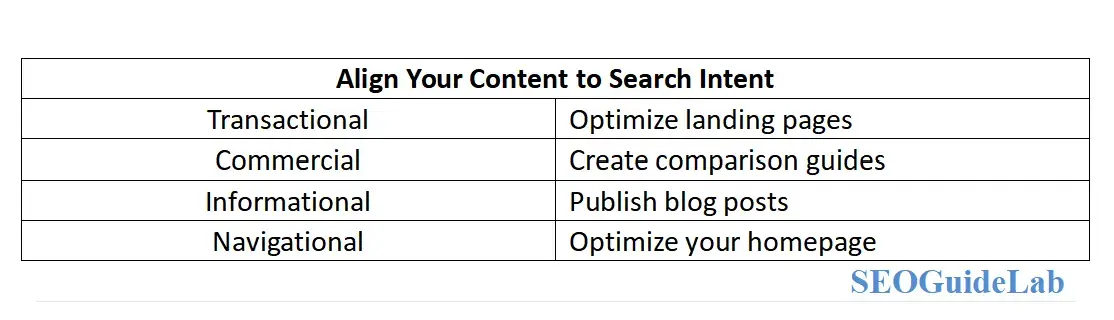
Transactional Intent: Focus on optimizing your landing pages, product pages, or service pages. Make sure they are designed to convert visitors into customers with strong calls to action (CTAs) and easy navigation.
Commercial Intent: Create detailed comparison guides, product reviews, or service comparisons that help users make informed decisions. You want to position your brand as an authority in the space.
Informational Intent: Publish high-quality blog posts, how-to articles, or educational resources. Ensure your content answers the user’s question in a detailed and helpful manner.
Navigational Intent: Ensure that your homepage and brand pages are optimized and clearly identifiable. Users searching with navigational intent should be able to easily find and navigate your website.
Bonus Tip: If You’re Unsure, Google It
If you’re ever in doubt about the intent behind a keyword, the easiest way to figure it out is by performing a Google search. Analyze the first page of results and see what type of content is ranking. This will give you a pretty good idea of what Google considers most relevant for that search.
Why SEO Without Search Intent is Like Guessing
SEO without understanding search intent is like throwing darts blindfolded. Sure, you might hit the target occasionally, but you won’t have the precision to consistently drive traffic or conversions. When you target high-intent keywords, you’re more likely to attract qualified leads who are ready to take action.
Google’s algorithm ranks content based on how well it satisfies search intent, not just how optimized it is. That’s why understanding search intent is so critical to your SEO success. So, always check the SERPs before creating content, and align your strategy with what the user truly wants.
By focusing on search intent analysis, you’ll not only boost your rankings but also improve your overall SEO performance and achieve better results in the long run.