How to do Keyword Research?
Introduction:
Why Keyword Research is Non-Negotiable? Imagine navigating a maze without a map—frustrating, time-consuming, and ineffective. This mirrors creating content without keyword research. SEO (search engine optimization) requires precision, not guesswork. Terms like “SEO meaning” or “what is SEO” aren’t just jargon; they’re clues revealing how audiences seek solutions.
Real-World Impact:
Case Study 1: A tech blog targeting “how to fix slow laptops” tripled organic traffic in 3 months.
Case Study 2: A local bakery using “vegan cupcakes Chicago” saw a 150% rise in store visits.
The Keyword Bridge: Without keywords, even stellar content remains invisible.
Step 1: Uncover Audience Needs Like a Detective
Tools to Dig Deeper
AnswerThePublic: Generates question-based keyword clouds (e.g., “Why does SEO matter?”).
Google Trends: Analyzes seasonal spikes (e.g., “Halloween costumes 2023”).
Reddit AMAs: Uncovers niche discussions.
Step-by-Step Persona Creation:
1. Demographics: Age, location, profession.
2. Pain Points: Challenges (e.g., “low blog traffic”).
3. Search Behavior: Preferred platforms (Google vs. YouTube).
Actionable Tip: Host surveys using Typeform to validate assumptions.
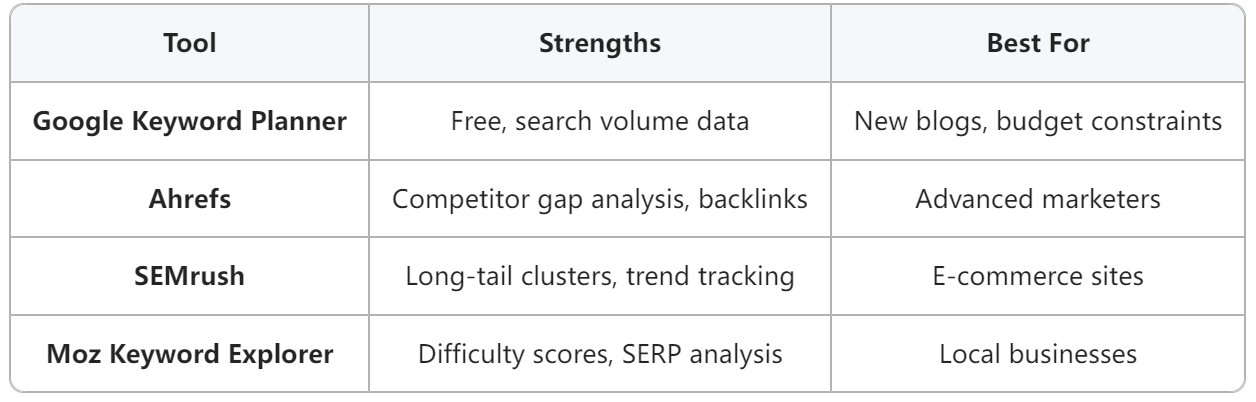
Step 2: Expand Keyword Lists with Surgical Precision
A. Free vs. Premium Tools Compared
Long-Tail Gems:
· Example: “How to optimize WordPress SEO without plugins” has 1/5th the competition of “WordPress SEO.”
B. Local SEO Strategies
· Geo-Targeting: “Emergency plumber [City Name]” outperforms generic terms.
· Google My Business: Embed keywords in business descriptions.
Local Success Story: A Miami-based florist ranked for “same-day flower delivery Miami Beach,” boosting orders by 120%.
Step 3: Align Keywords with Search Intent
The 4 Intent Categories
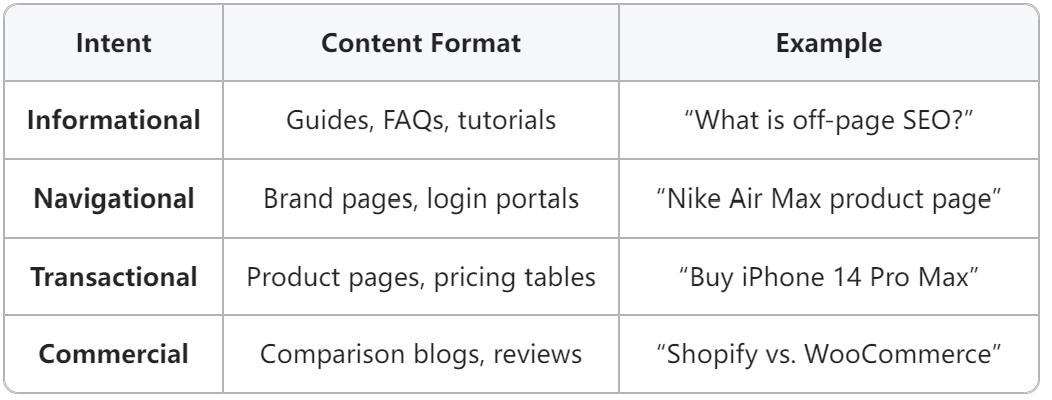
Intent-First Content Example:
· Search Query: “How to start a podcast”
· Optimal Content: A step-by-step guide with podcast hosting comparisons.
Step 4: Ethical Competitor Analysis
A. Reverse-Engineer Competitor Success
1. Identify Top Competitors via SimilarWeb or SEMrush.
2. Analyze Their Top Pages: Tools like Ahrefs’ Site Explorer.
3. Spot Content Gaps: Topics they miss (e.g., video tutorials).
Case Study: A SaaS company discovered competitors neglected “CRM for small teams.” They created a pillar page, ranking #1 in 8 weeks.
B. Backlink Mining
1. Export competitors’ backlinks using Ahrefs.
2. Target high-authority domains for outreach.
Pro Tip: Tools like Pitchbox streamline link-building outreach.
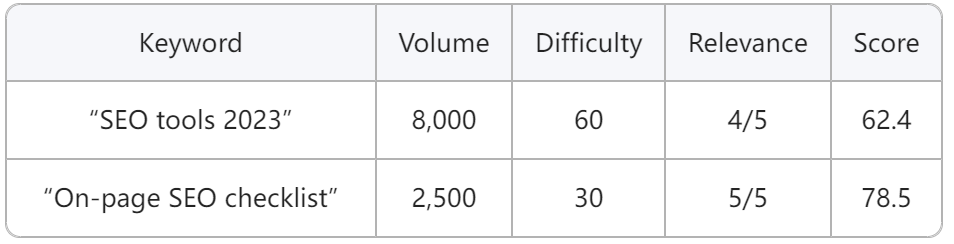
Step 5: Score and Prioritize Keywords
The Keyword Scoring Formula
Score = (Search Volume × 0.4) + (Relevance × 0.4) + (100 − Difficulty × 0.2)
Seasonal Opportunities
Use Google Trends to capitalize on events (e.g., “tax software” peaks in March).
Step 6: Map Keywords to a Content Ecosystem
The Pillar-Cluster Model
1. Pillar Page: Broad topic (“Ultimate SEO Guide”).
2. Cluster Content: Subtopics like “On-page SEO,” “Keyword Research.”
Internal Linking: Link clusters to pillar pages to boost authority.
Content Calendar Templates
· Monthly Focus:
o Week 1: Publish pillar content.
o Week 2–3: Create cluster blogs.
o Week 4: Audit and update old posts.
Free Template: [Link to Google Sheets content calendar].
7 Common Keyword Mistakes (and Fixes)
1. Ignoring Long-Tail Keywords
o Use AnswerThePublic for question-based phrases.
2. Overlooking Mobile Intent
o Optimize for voice search (“OK Google, best pizza near me”).
3. Keyword Cannibalization
o Audit duplicate keywords with Screaming Frog.
4. Static Keyword Lists
o Quarterly reviews using Google Analytics.
5. Neglecting Local SEO
o Embed city names in meta descriptions.
6. Forgetting Semantic SEO
o Integrate LSI keywords like “search rankings” or “organic traffic.”
7. Over-Optimization
o Maintain keyword density below 2%.
Advanced Tactics for 2025
AI-Powered Keyword Clustering
Tools like Frase.io group related terms (e.g., “SEO tips” + “SEO best practices”).
Featured Snippet Optimization
· Target Position 0 with concise answers (40–60 words).
· Example:
Q: What is on-page SEO?
A: On-page SEO optimizes individual webpages via keywords, headers, and meta tags to rank higher on search engines.
Optimizing for Voice Search
· Natural Language: Use conversational phrases (“How do I…?”).
· Local Focus: “Where can I find a 24-hour gym nearby?”
Voice Search Case Study: A recipe blog added voice-friendly content, increasing mobile traffic by 65%.
FAQ: Answering Top Keyword Questions
Q1: How often should I update keywords?
A: Audit every 3 months; adjust for algorithm updates (e.g., Google’s BERT).
Q2: What’s the ideal keyword length?
A: Mix short-tail (1–2 words) and long-tail (3–5 words).
Q3: Is keyword research different for e-commerce?
A: Yes. Focus on buyer intent (e.g., “buy,” “price,” “review”).
Q4: How do I recover from keyword cannibalization?
A: Merge duplicate pages or add canonical tags.
Q5: Can I rank without backlinks?
A: Possible but unlikely. Quality backlinks remain critical.
Conclusion: Transform Keywords into Revenue
Keyword research isn’t a checklist—it’s cyclical. Success demands continuous testing, adapting, and refining. Start small: Pick 10 keywords, create intent-aligned content, and track rankings.