What Are URL Parameters? How They Impact SEO - SEOGuideLab
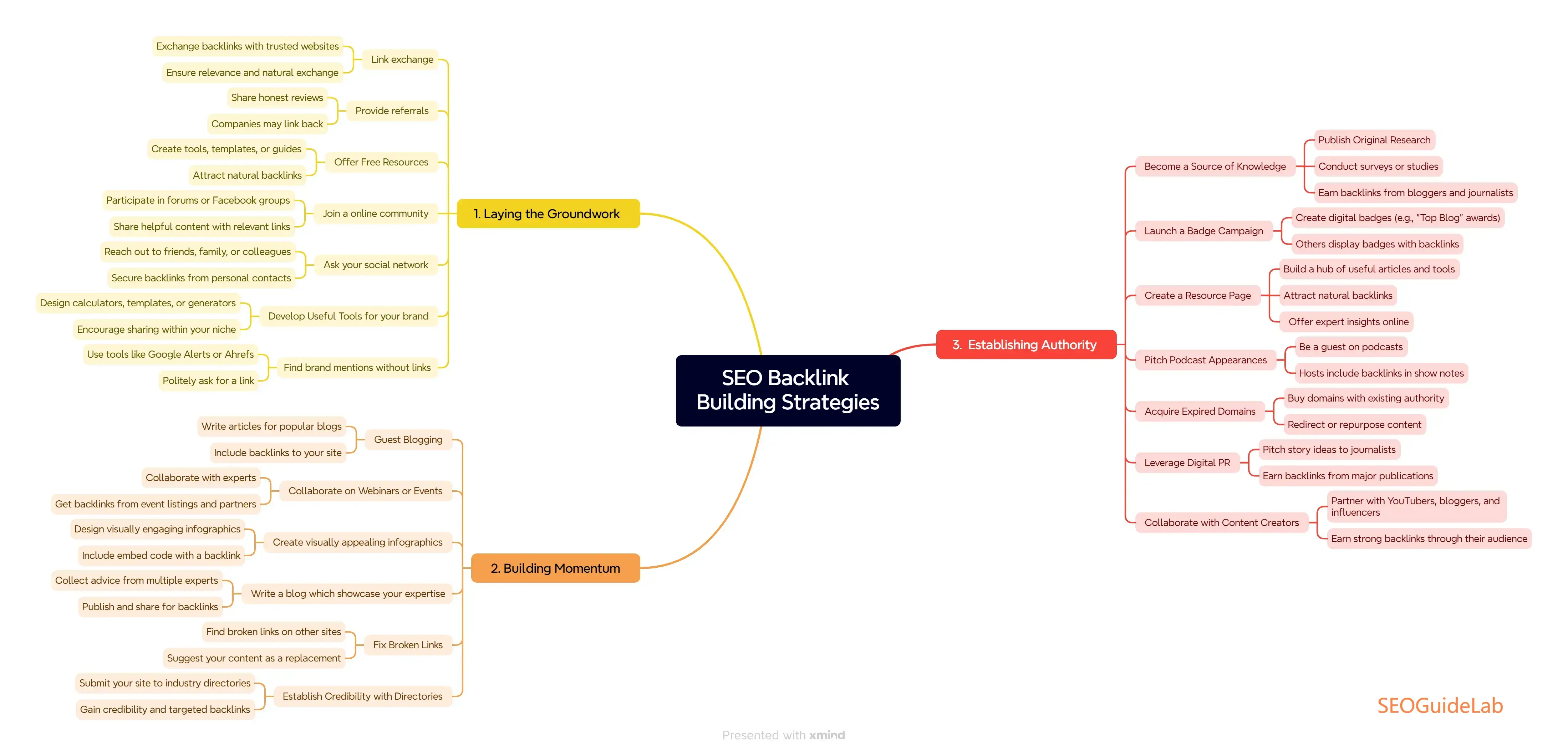
Introduction
Ever clicked on a link that looked like this — https://example.com/products?category=shoes&utm_source=google — and wondered what all that extra stuff means? You're not alone.
Those confusing-looking bits that come after the question mark are known as URL parameters. And while they may look like digital gibberish, they serve important functions. URL parameters are a powerful tool — but they can also cause SEO headaches if misused.
For SEO beginners, understanding how URL parameters work is essential. Improper handling can lead to duplicate content, indexing issues, and a wasted crawl budget — all of which can hurt your site’s visibility in search engines.
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about URL parameters — what they are, how they work, how they affect SEO, and what best practices you should follow to keep your site in top shape.
Let’s dive in.
What Are URL Parameters?
Basic Definition
URL parameters (also called query strings) are the parts of a URL that come after a question mark (?). They help pass information about a user’s activity or preferences to a website.
For example:
https://example.com/products?category=shoes
Here, category=shoes is a URL parameter telling the website to show shoe products.
URL parameters are made up of key-value pairs, like key=value. You can include multiple parameters in one URL by separating them with an ampersand (&):
?category=shoes&color=blue&sort=price_asc
Common Types of URL Parameters
Beginners will often run into these types of parameters:
Tracking parameters
– e.g.,
utm_source=google(used in marketing to track traffic sources)
Session IDs
– e.g.,
?sessionid=123abc(used to keep track of user sessions)
Sorting or filtering
– e.g.,
?sort=price_ascor?filter=red(used on eCommerce sites)
Pagination
– e.g.,
?page=2(for navigating through pages of content)
Search queries
– e.g.,
?q=sneakers(used for internal search results)
These parameters help websites deliver customized content, but they can cause problems if not handled properly.
How URL Parameters Work
URL Structure Explained
Let’s break down a basic URL:
https://www.example.com/products?category=shoes&page=2
https://— protocolwww.example.com— domain/products— path?category=shoes&page=2— parameters
These parameters are often dynamically added based on user actions, like selecting a category or using a filter on a shopping site.
Query Strings and Key-Value Pairs
Each parameter in the query string has a key (what kind of information) and a value (the specific data). For instance:
category=shoes→ key:category, value:shoespage=2→ key:page, value:2
When multiple parameters are present, they’re joined by the & symbol:?category=shoes&sort=price_asc&page=2
These parameters help personalize the experience, but they change the actual URL — which brings us to their SEO impact.
Why URL Parameters Matter in SEO
Duplicate Content Issues
Imagine you have the following URLs:
example.com/productsexample.com/products?sort=price_ascexample.com/products?page=2
Even though they all point to similar content, search engines might treat them as separate pages, creating duplicate content issues. This can dilute your SEO power because search engines won’t know which version to prioritize.
Crawl Budget Waste
Crawl budget is the number of pages Googlebot crawls on your site within a given time. If your site has thousands of parameterized URLs, search engines may waste time crawling unnecessary versions, skipping the important ones.
For example:
example.com/products?color=blueexample.com/products?color=redexample.com/products?color=green
If these pages show very similar content, it’s better to consolidate them.
Indexing Challenges
Google might index the wrong version of your page, especially if parameters are used inconsistently. This can hurt rankings or lead users to outdated or irrelevant pages.
To avoid this, you’ll need tools like canonical tags, which we’ll explore shortly.
Tracking vs SEO Conflicts
UTM parameters (used for marketing) like ?utm_source=facebook are great for tracking — but they can create multiple versions of the same page in search engine indexes if left unchecked.
How Google Handles URL Parameters
Google’s View on Parameters
Google is aware of the complexity URL parameters can cause and tries to cluster parameterized URLs together. However, it’s not perfect.
According to Google’s documentation, site owners can help by configuring parameter behavior in Google Search Console.
Using Google Search Console for Parameter Handling
In the old version of Search Console, there was a URL Parameters tool allowing you to tell Google how to handle specific parameters. While it’s no longer available, understanding this concept is still helpful.
Now, Google recommends using canonical tags and robots.txt directives.
Canonical Tags and URL Parameters
A canonical tag tells Google which version of a URL is the "master" copy. So even if multiple URLs exist:
example.com/productsexample.com/products?utm_source=google
The canonical tag on both pages should point to:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/products">
This helps consolidate ranking signals and avoid duplication.
Best Practices for Managing URL Parameters
Use Descriptive and Consistent Parameters
Stick to clear names like utm_campaign instead of vague ones like c123. It helps both SEO tools and marketers understand what each parameter does.
Avoid Parameter Overload
Using too many parameters in a single URL looks messy and confuses both users and search engines:
Bad: example.com/page?c=12&a=32&b=47&q=hello&x=abc
Keep it simple and structured.
Implement Proper Canonicalization
Always point to the original version of the content using the canonical tag. This tells Google which page to rank and helps consolidate link equity.
Use Robots.txt Carefully
If certain parameterized pages don’t need to be crawled, you can block them using robots.txt, but proceed with caution. Blocking too much can hide important content from search engines.
Leverage Google Search Console Insights
Monitor crawl stats and indexing reports to detect when parameterized URLs are showing up unexpectedly. Fix issues early to avoid long-term damage.
Use Server-Side URL Rewrites
Convert messy URLs into clean, readable versions using server-side rewriting. For example:
From:
example.com/products?category=shoesTo:
example.com/products/shoes
This is better for SEO and user experience.
URL Parameters vs Clean URLs
SEO Perspective
Clean URLs like example.com/shoes are typically better for SEO than parameterized ones. They’re easier to read, link to, and share.
However, parameters are sometimes necessary — especially on eCommerce sites — so use them wisely.
User Experience Considerations
Long, messy URLs can look suspicious or untrustworthy. Clean URLs improve the click-through rate (CTR) from search results and build credibility.
Final Thoughts
URL parameters may seem like a small detail, but they have a big impact on your SEO. When used improperly, they can lead to duplicate content, crawl inefficiencies, and lost rankings. But with the right strategy — including clear parameter naming, canonical tags, and regular audits — they can be managed effectively.
If you’re just starting your SEO journey, take the time to understand how your website uses parameters. Small fixes here can lead to big gains in the long run.
Next Steps:
Check your most important pages — are they using URL parameters?
Use tools like Google Search Console and Screaming Frog to audit parameter use.
Add canonical tags where needed to consolidate your SEO value.
For more beginner-friendly guides, check out our articles on [Canonical URLs Explained] and [How to Optimize Crawl Budget]